
This is a complete tutorial for beginners on how to develop a Java project using Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA, and PostgreSQL from scratch. This tutorial will help you understand basic concepts, configurations, tools required, and coding to execute a simple API application with Create, Read, Update, and Delete functionalities (CRUD operation).
This article can be divided mainly into 2 sections.
- One, Tools setup
- Two, Coding + concepts (CRUD), you are here 😊
Continue if you’ve gone through the environment setup and are ready to code. If not, click on the link below 😊
Java Spring Boot with PostgreSQL — CRUD API Project: Part 1/2 (Tools Installation)
1. Open VS Code
2. Edit pom.xml file
Ensure you have the following dependencies in the pom.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>employer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>employer</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. Edit application.properties file
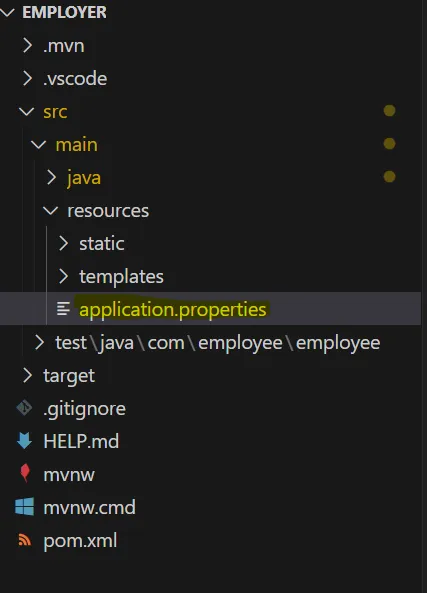
spring.application.name=employer
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/employer
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=postgres
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
#jpa vendor adapter configuration
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
server.port=8084- employer is the name of the database we will be creating in PostgreSQL
- The server port number is the port address used to trigger the API call
4. Create the green-highlighted folders
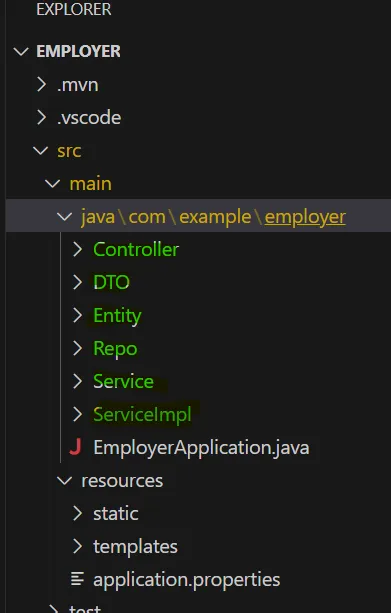
5. Create the following files under the DTO folder
EmployerDTO.java
package com.example.employer.DTO;
public class EmployerDTO {
private int employerID;
private String employerName;
private String employerEmail;
public EmployerDTO(int employerID, String employerName, String employerEmail) {
this.employerID = employerID;
this.employerName = employerName;
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
public EmployerDTO() {
}
public int getEmployerID() {
return employerID;
}
public void setEmployerID(int employerID) {
this.employerID = employerID;
}
public String getEmployerName() {
return employerName;
}
public void setEmployerName(String employerName) {
this.employerName = employerName;
}
public String getEmployerEmail() {
return employerEmail;
}
public void setEmployerEmail(String employerEmail) {
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
" employerID='" + getEmployerID() + "'" +
", employerName='" + getEmployerName() + "'" +
", employerEmail='" + getEmployerEmail() + "'" +
"}";
}
}EmployerSaveDTO.java
package com.example.employer.DTO;
public class EmployerSaveDTO {
private String employerName;
private String employerEmail;
public EmployerSaveDTO(String employerName, String employerEmail) {
this.employerName = employerName;
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
public EmployerSaveDTO() {
}
public String getEmployerName() {
return employerName;
}
public void setEmployerName(String employerName) {
this.employerName = employerName;
}
public String getEmployerEmail() {
return employerEmail;
}
public void setEmployerEmail(String employerEmail) {
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
" employerName='" + getEmployerName() + "'" +
", employerEmail='" + getEmployerEmail() + "'" +
"}";
}
}EmployerUpdateDTO.java
package com.example.employer.DTO;
public class EmployerUpdateDTO {
private int employerID;
private String employerName;
private String employerEmail;
public EmployerUpdateDTO(int employerID, String employerName, String employerEmail) {
this.employerID = employerID;
this.employerName = employerName;
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
public EmployerUpdateDTO() {
}
public int getEmployerID() {
return employerID;
}
public void setEmployerID(int employerID) {
this.employerID = employerID;
}
public String getEmployerName() {
return employerName;
}
public void setEmployerName(String employerName) {
this.employerName = employerName;
}
public String getEmployerEmail() {
return employerEmail;
}
public void setEmployerEmail(String employerEmail) {
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
" employerID='" + getEmployerID() + "'" +
", employerName='" + getEmployerName() + "'" +
", employerEmail='" + getEmployerEmail() + "'" +
"}";
}
}6. Create the following file under the Entity folder
Employer.java
package com.example.employer.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employer")
public class Employer {
@Id
@Column(name = "employer_id", length = 10)
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int employerID;
@Column(name = "employer_name", length = 50)
private String employerName;
@Column(name = "employer_email", length = 60)
private String employerEmail;
public Employer(int employerID, String employerName, String employerEmail){
this.employerID = employerID;
this.employerName = employerName;
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
public Employer(String employerName, String employerEmail){
this.employerName = employerName;
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
public Employer(){
}
public int getEmployerID() {
return employerID;
}
public void setEmployerID(int employerID) {
this.employerID = employerID;
}
public String getEmployerName() {
return employerName;
}
public void setEmployerName(String employerName) {
this.employerName = employerName;
}
public String getEmployerEmail() {
return employerEmail;
}
public void setEmployerEmail(String employerEmail) {
this.employerEmail = employerEmail;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
" employerID='" + getEmployerID() + "'" +
", employerName='" + getEmployerName() + "'" +
", employerEmail='" + getEmployerEmail() + "'" +
"}";
}
}7. Create the following file under the Repo folder
EmployerRepo.java
package com.example.employer.Repo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.example.employer.Entity.Employer;
@EnableJpaRepositories
@Repository
public interface EmployerRepo extends JpaRepository<Employer, Integer>{
}8. Create the following file under the Service folder
EmployerService.java
package com.example.employer.Service;
import java.util.List;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerDTO;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerSaveDTO;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerUpdateDTO;
public interface EmployerService {
List<EmployerDTO> getAllEmployers();
String addEmployer(EmployerSaveDTO employerSaveDTO);
String updateEmployer(EmployerUpdateDTO employerUpdateDTO);
String deleteEmployer(int employerID);
}9. Create the following file under the ServiceImpl folder
EmployerServiceImpl.java
package com.example.employer.ServiceImpl;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerDTO;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerSaveDTO;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerUpdateDTO;
import com.example.employer.Entity.Employer;
import com.example.employer.Repo.EmployerRepo;
import com.example.employer.Service.EmployerService;
@Service
public class EmployerServiceImpl implements EmployerService {
@Autowired
private EmployerRepo employerRepo;
@Override
public List<EmployerDTO> getAllEmployers() {
List<Employer> employerList = employerRepo.findAll();
List<EmployerDTO> employerDTOList = new ArrayList<>();
for(Employer employer : employerList){
EmployerDTO employerDTO = new EmployerDTO(employer.getEmployerID(), employer.getEmployerName(), employer.getEmployerEmail());
employerDTOList.add(employerDTO);
}
return employerDTOList;
}
@Override
public String addEmployer(EmployerSaveDTO employerSaveDTO) {
Employer employer = new Employer(employerSaveDTO.getEmployerName(), employerSaveDTO.getEmployerEmail());
employerRepo.save(employer);
return employer.getEmployerName();
}
@Override
public String updateEmployer(EmployerUpdateDTO employerUpdateDTO) {
if(employerRepo.existsById(employerUpdateDTO.getEmployerID())){
Employer employer = employerRepo.getById(employerUpdateDTO.getEmployerID());
employer.setEmployerName(employerUpdateDTO.getEmployerName());
employer.setEmployerEmail(employerUpdateDTO.getEmployerEmail());
employerRepo.save(employer);
return "Updated Employer ID: " + employerUpdateDTO.getEmployerID();
}else{
return "Employer ID not present";
}
}
@Override
public String deleteEmployer(int employerID) {
if(employerRepo.existsById(employerID)){
employerRepo.deleteById(employerID);
return "Employer ID deleted: " + employerID;
}else{
return "Employer ID not present";
}
}
}10. Create the following file under the ServiceImpl folder
EmployerController.java
package com.example.employer.Controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerDTO;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerSaveDTO;
import com.example.employer.DTO.EmployerUpdateDTO;
import com.example.employer.Service.EmployerService;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
@RequestMapping("api/v1/employer")
public class EmployerController {
@Autowired
private EmployerService employerService;
@GetMapping(path = "/getAllEmployers")
public List<EmployerDTO> getAllEmployers(){
return employerService.getAllEmployers();
}
@PostMapping(path = "/add")
public String addEmployer(@RequestBody EmployerSaveDTO employerSaveDTO){
return employerService.addEmployer(employerSaveDTO);
}
@PutMapping(path = "/update")
public String updateEmployer(@RequestBody EmployerUpdateDTO employerUpdateDTO){
return employerService.updateEmployer(employerUpdateDTO);
}
@DeleteMapping(path = "/delete/{employerID}")
public String deleteEmployer(@PathVariable(value = "employerID") int employerID){
return employerService.deleteEmployer(employerID);
}
}11. Edit the EmployerApplication.java file as below
package com.example.employer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class EmployerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EmployerApplication.class, args);
}
}12. Final structure
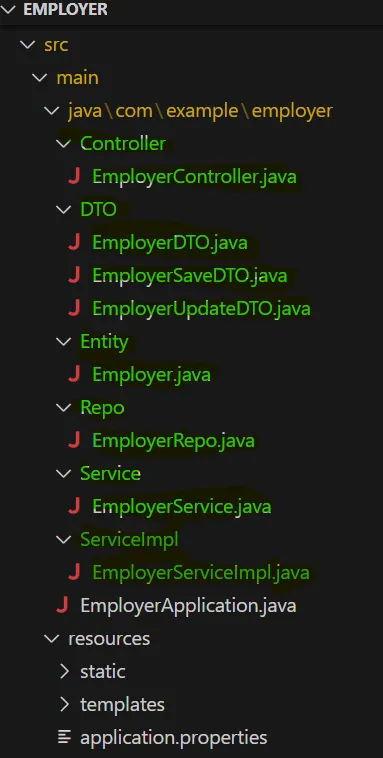
13. Run the following command in Git Bash to create an employer database
CREATE DATABASE employer WITH ENCODING='UTF8';14. Open DBeaver
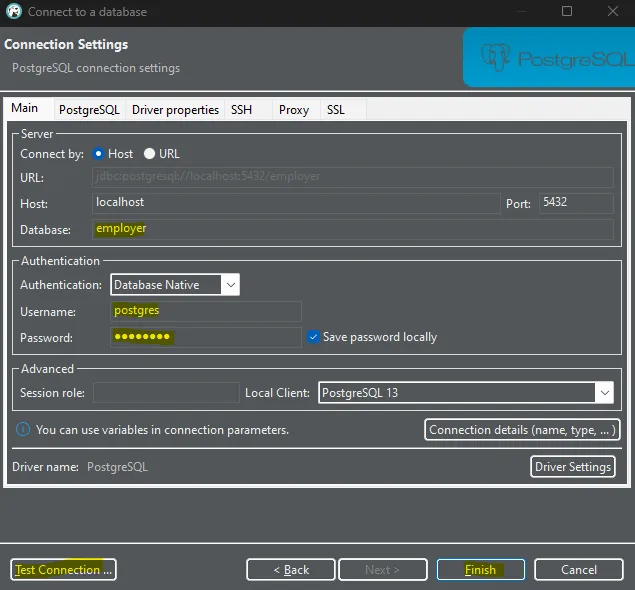
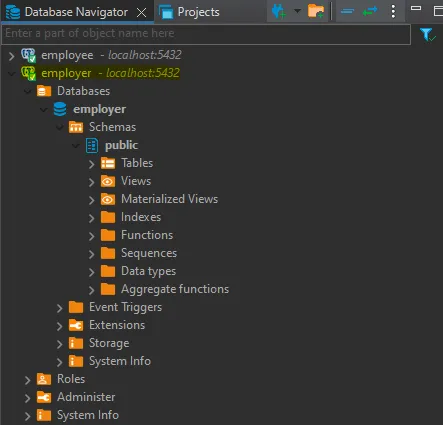
15. Run the project in VS Code
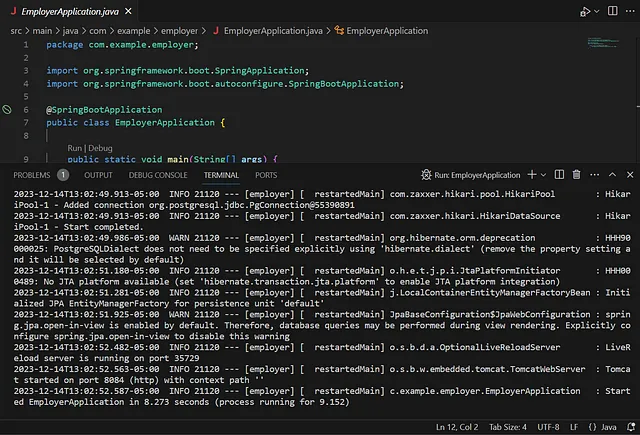
If the Project build is successful and error-free, the server starts smoothly
16. Open Postman
To add a new employer
Authorization — Type → No Auth
Headers — Content-Type → application/json
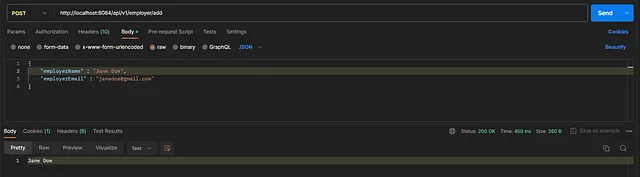
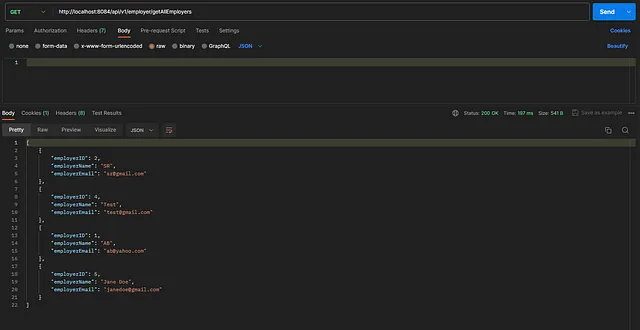
To list all added employers
Authorization — Type → No Auth
To update an employer’s details
Authorization — Type → No Auth
Headers — Content-Type → application/json
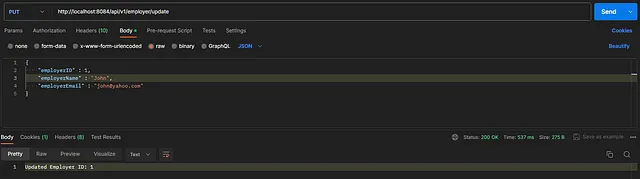
To delete an employer
Authorization — Type → No Auth
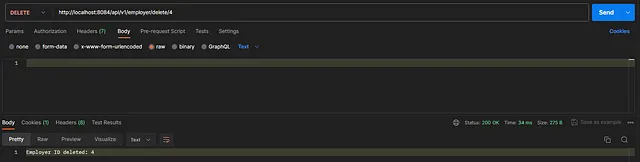
17. Open DBeaver to verify the results
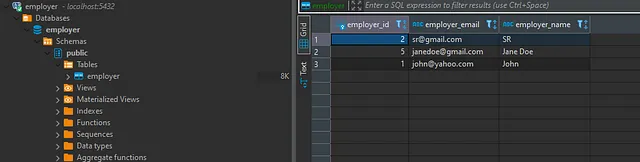
Thus, we come to an end of CRUD operations using Spring Boot and PostgreSQL😊

Thank you for reading! I hope you’re able to understand and proceed with the development of this explanation and if so, please share to help others too. 😊
Well, there are a lot of areas for improvement in this project and, for any new suggestions or comments, I’m all ears.
Download project from: https://github.com/sharuroy16/employer
